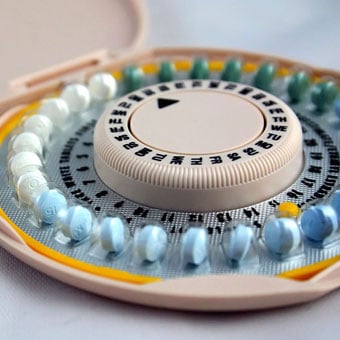
Birth control pills can be an effective method to prevent pregnancy.Source: Getty Images
Things to know about birth control
- Birth control methods can be broadly classified into barrier methods (that prevent sperm cells from reaching the egg), methods that prevent ovulation such as the birth control pill, and methods that allow fertilization of the egg but prevent implantation of the fertilized egg inside the uterus (womb) such as the IUD (intrauterine device).
- Condoms and diaphragms are examples of barrier birth control methods.
- Birth control pills are an example of a hormonal birth control method that prevents ovulation.
- The decision about what kind of birth control option to use is extremely personal, and there is no single choice that is safest or best for all women or couples.
- A woman should carefully weigh the risks and benefits, along with the effectiveness of each method before choosing a birth control method. A thorough and open discussion with a health care professional can help in this decision process.
- Different forms of birth control have different side effects and risk profiles.
- The choice of the birth control method depends on many factors, such as the desire for reversible birth control (preserving future fertility) or permanent birth control methods (surgical sterilization). Some birth control methods, such as barrier methods, may offer some protection against sexually transmitted diseases (STDs), while most methods do not.
- No method of birth control is 100% effective in preventing STDs.
- Some birth control methods have higher effectiveness rates than others, but no method of birth control is 100% effective in every case.
Birth Control Types
Doctor’s View on Birth Control Types
Birth control can be permanent or temporary. The woman and her partner, taking into consideration the ease of use, side effects, costs, and effectiveness of each method, must weigh the pros and cons of various birth control types.
- Reversible methods of birth control
- Permanent methods of birth control
- Emergency contraception
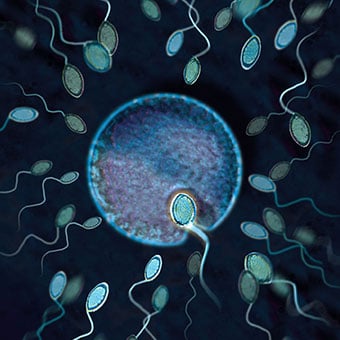
Some birth control methods stop sperm from reaching the egg, preventing fertilization. Barrier methods of birth control prevent the man’s sperm from reaching an egg.Source: Getty Images
What is birth control, and how does it work?
Birth control works to prevent pregnancy in different ways.
- Hormonal birth control methods work by preventing ovulation so that a woman is temporarily infertile.
- Barrier methods of birth control prevent the man’s sperm from reaching an egg.
- Barrier methods include:
- diaphragms,
- condoms, and
- cervical caps.
- Spermicide is a chemical that destroys sperm to prevent them from reaching the egg.
- Birth control methods such as intrauterine devices work by preventing a fertilized egg from implanting in the uterus and causing a pregnancy.

Birth control is not 100% effective, so it is possible to get pregnant while using most types of contraceptives. Their effectiveness depends upon the time in your monthly cycle when you begin using the contraception.Source: iStock
How long does it take for birth control to begin working?
- Some kinds of birth control start to work with the first use, such as barrier methods.
- Hormonal methods of birth control such as pills, implants, or the patch may not begin working immediately.
- Their effectiveness depends upon the time in your monthly cycle when you begin using the contraception.
- Sometimes it is recommended that women use an alternate method of contraception for the first week after beginning the pill or hormonal contraception.
Can you get pregnant on birth control?
There is no form of birth control that is 100% effective, so it is possible to get pregnant while using most types of birth control. However, many types of birth control, when used correctly, are highly effective in preventing pregnancy. For example, the birth control pill is over 99% effective in preventing pregnancy when taken correctly. For all forms of birth control, it is important to have a basic understanding of how they work and how to use them correctly.

There are many birth control options for both men and women. Permanent methods (surgical sterilization) are also available for those who no longer desire to have children.Source: iStock
What are the different types of birth control available?
Types of birth control methods include options that prevent sperm from reaching an egg, known as barrier methods, methods that prevent ovulation, and methods that prevent implantation of a fertilized egg into the uterus. Permanent methods (surgical sterilization) are also available for those who no longer desire to have children.
Types of birth control
Hormonal birth control methods include:
- Birth control pills
- Hormonal patches
- Birth control implants
- Vaginal ring
Barrier birth control methods include:
- Diaphragms
- Condoms
- Cervical caps
- Spermicides
Natural birth control methods include the use of:
- Ovulation test kits
- Cervical mucus examination
- Tracking menstrual cycles (rhythm method)
Other types of birth control options include:
- Intrauterine devices
- Emergency contraception “morning after” pills
Surgical sterilization methods for birth control include:
- Tubal ligation (“tubes tied”)
- Vasectomy
QUESTION
Which of the following are methods for contraception? See Answer

Hormonal birth control pills prevent ovulation in women.Source: Getty Images
Hormonal birth control (birth control pills) types and side effects
Hormonal options of birth control involve the use of hormones to prevent ovulation in a woman. Although oral contraceptive pills are the most widely used hormonal method, other options are available including the vaginal ring, hormone patches applied to the skin, and injections of progestin (birth control shot).
Common side effects of birth control pills
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Weight gain
- Skin discoloration
- Acne
- Bleeding between periods or spotting
- Mood swings
- Change in menstrual flow
- Breast swelling or tenderness
Heart attacks, blood clots, and strokes are potential and serious complications of oral contraceptives.
Cigarette smoking increases the risk of these complications. This risk is greatest in women over 35 who are heavy smokers (>15 cigarettes/day). Your health-care professional l usually will recommend that you quit smoking if you use birth control pills.
Latest Women’s Health News
Daily Health News
Trending on MedicineNet

Barrier method birth control choices include condoms, diaphragms, and cervical caps.Source: Getty Images
Barrier methods of birth control (including condoms) types and side effects
Barrier options prevent fertilization of the egg by a sperm cell. These either prevent contact between egg and sperm via a physical block or kill sperm cells before they can fertilize an egg. Examples of physical barrier contraceptives include the diaphragm, condoms, and the cervical cap or shield.
Contraceptive sponges contain a spermicide cream to kill sperm cells, and other forms of spermicides are available as well. Spermicides may be used in combination with barrier methods for greater effectiveness.
Side effects of barrier methods of birth control
Side effects of barrier methods of birth control can include:
- An increased risk of developing urinary tract infections (UTIs) if using a diaphragm and spermicide.
- Leaving a diaphragm or cervical cap in for longer than 24 hours increases your risk for toxic shock syndrome.
- Some people may have allergies to the chemicals used in spermicide creams or other spermicide products. They may develop irritation of the vagina or penis.
One of the advantages of the use of barrier methods is that they can decrease the risk of sexually transmitted diseases (especially properly used condoms). None of them eliminates this risk.

SLIDESHOW
Choosing Your Birth Control Method See Slideshow

Vasectomies and tubal ligation offer a more permanent birth control solution.Source: Getty Images
Surgical sterilization (tubal ligation or vasectomy) side effects and risks
Surgical sterilization is a form of permanent birth control that is available for both women (tubal ligation) and men (vasectomy). Sterilization implants (a small coil is inserted into the fallopian tubes to block them) are a more recent type of permanent birth control that is available for women that allow women to avoid the surgical procedure associated with tubal ligation.
What are the risks of a vasectomy or tubal ligation?
Although women who have had tubal ligation do not have side effects after recovering from the procedure, any surgery itself carries a small risk of infection or bleeding as well as complications from the anesthetic agents.
Likewise, the vasectomy procedure is associated with small risks from the procedure as well as some swelling and pain in the days following the procedure. For some time post-vasectomy, a man can still be fertile and it is usually recommended that a barrier method or other birth control method is used for 10-12 weeks or 15 to 20 ejaculations post-procedure.
Subscribe to MedicineNet’s General Health Newsletter
By clicking Submit, I agree to the MedicineNet’s Terms & Conditions & Privacy Policy and understand that I may opt out of MedicineNet’s subscriptions at any time.

Ovulation tracking is the least successful birth control method.Source: iStock
Natural birth control methods
Natural methods involve tracking a woman’s menstrual cycle to try to determine when ovulation is most likely to occur and avoiding sexual intercourse (or using barrier contraceptives) during that time. There are different ways to detect ovulation, including the basal body temperature method (ovulation causes a slight increase in basal body temperature) and the use of home ovulation test kits. Checking and recording the consistency of cervical mucus is another way to help determine when ovulation occurs.
These methods tend to be the least successful methods as they require discipline in recording and tracking and understanding the results.

Emergency contraceptive pills are becoming more accessible to patients.Source: Getty Images
Emergency contraception types and side effects
Emergency contraception is a medication or device used to prevent pregnancy after unprotected intercourse has occurred. Emergency hormonal contraceptives are sometimes known as “morning-after” pills. These drugs prevent pregnancy if taken within 72 hours after intercourse. This is also known as emergency contraception. Insertion of a copper intrauterine device (IUD) is also an effective method of emergency contraception.
Side effects of emergency contraception (morning after pill)
Side effects of emergency contraception or “morning after” pills can include
From 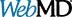
Women’s Health Resources
Featured Centers
Health Solutions From Our Sponsors

Intrauterine devices (IUDs) are a long-term, yet impermanent, birth control method.Source: iStock
IUDs (intrauterine devices) side effects
IUDs or intrauterine devices are implantable devices that create an environment in the lining tissues of the womb that is unfavorable for the implantation of a fertilized egg.
Side effects of IUDs depend on the type of IUD being used.
- Copper-containing IUDs may worsen menstrual bleeding and cramps.
- Puncture or perforation of the uterus is a rare complication of all IUDs.
- IUDs that contain hormones may cause similar side effects to hormonal contraceptives, like headaches, breast tenderness, or acne.
Medically Reviewed on 5/18/2022
References
United States. WomensHealth.gov. “Birth control methods.” Apr. 24, 2017. <https://www.womenshealth.gov/publications/our-publications/fact-sheet/birth-control-methods.html>.